1. Carbonaceous aerosols from boreal forest fires and implications for radiative forcing
Objectives:
- Understand the emission and fate of brown carbon (BrC) and black carbon from boreal forest fires;
- Examine the impact of boreal forest fires on radiative forcing
Approach:
- Measure the optical properties of BrC in the field and lab;
- Use intensive field/satellite observations to evaluate model representation of brown carbon and ozone;
- Use global climate model to predict future air pollution influenced by projected biomass burning emissions.
People:
- Kunal Bali (PhD student), James Campbell (PhD student) and collaborators including L.-W. Antony Chen (U of Nevada) and Judy Chow (DRI).
Funding:
- NSF
Reference:
- Nicole June, Xuan Wang, L.-W. Antony Chen, Judith C. Chow, John G. Watson, Xiaoliang Wang, Barron H. Henderson, Yiqi Zheng, Jingqiu Mao: Spatial and temporal variability of brown carbon in United States: implications for direct radiative effects, Geophysical Research Letters, 47, e2020GL090332. https://doi. org/10.1029/2020GL090332 (link).
- L.-W. Antony Chen, Judith C. Chow, Xiaoliang Wang, Junji Cao, Jingqiu Mao, and John G. Watson: Brownness of Organic Aerosol over the U.S.: Evidences for Seasonal Biomass Burning and Photobleaching Effects, Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c08706.
(photo courtesy of Cameron McNaughton)
2. Wintertime aerosol pollution in Fairbanks
Objectives:
- Understand multiphase chemistry of hydroxymethanesulfonate (HMS)
- Understand sulfate formation mechanisms in Fairbanks winter.
Approach:
- Use field observations and models to examine possible HMS chemistry in ambient aerosols and cloud;
People:
- James Campbell (PhD student), and collaborators including Rodney Weber (Georgia Tech), Jason St. Clair (UMBC/NASA), and Bill Simpson (UAF).
Funding:
- NSF
Reference:
- Mao J., Fan, S., Jacob, D. J., and Travis, K. R.: Radical loss in the atmosphere from Cu-Fe redox coupling in aerosols, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 13, 509-519, doi:10.5194/acp-13-509-2013, 2013 (link).
- Mao, J., Fan, S., and Horowitz, L. W.: Soluble Fe in Aerosols Sustained by Gaseous HO2 Uptake, Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 4, 98-104, 10.1021/acs.estlett.7b00017, 2017. (link)
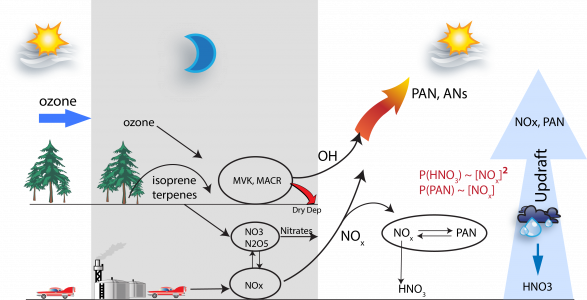
3. Anthropogenic influences on biogenic secondary organic aerosol
Objectives:
- Quantify the yields of oxygenated VOCs from oxidation of biogenic VOCs and their contribution to aerosols;
- Better understand ozone formation from oxidation of BVOCs under different NOx regimes;
- Evaluate the role of biogenic VOCs in climate system
Approach:
- Use intensive field/satellite observations to evaluate model representation of BVOC oxidation;
- Use multidecadal observations to evaluate model representation of ozone and aerosols resulting from emission changes;
- Use global climate model to simulate future air pollution in different future scenarios.
People:
- Yiqi Zheng, and collaborators including Larry Horowitz(GFDL), Vaishali Naik (GFDL), Sally Ng (Georgia Tech), Joel Thornton (U Washington) and Havala Pye (EPA).
Funding:
- NOAA Climate Program Office.
Reference:
- Zheng, Y., Thornton, J. A., Ng, N. L., Cao, H., Henze, D. K., McDuffie, E. E., Hu, W., Jimenez, J. L., Marais, E. A., Edgerton, E., and Mao, J.: Long-term observational constraints of organic aerosol dependence on inorganic species in the southeast US, Atmos. Chem. Phys. , https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-2020-575, 2020 (link).
- Li., J. , J. Mao, Fiore, A. M., Cohen, R. C., Crounse, J. D., Teng, A. P., Wennberg, P. O., Lee, B. H., Lopez-Hilfiker, F. D., Thornton, J. A., Peischl, J., Pollack, I. B., Ryerson, T. B., Veres, P., Roberts, J. M., Neuman, J. A., Nowak, J. B., Wolfe, G. M., Hanisco, T. F., Fried, A., Singh, H. B., Dibb, J., Paulot, F., and Horowitz, L. W.: Decadal change of summertime reactive nitrogen species and surface ozone over the Southeast United States, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 2018.
- Li., J. , J. Mao, R. A. Washenfelder, S. S. Brown , J. Kaiser, F. N. Keutsch, R. Volkamer, G. M. Wolfe and coauthors , Observational constraints on glyoxal production from isoprene oxidation and its contribution to organic aerosol over the Southeastern United States, Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 121(16), 9849-9861, doi:10.1002/2016JD025331.
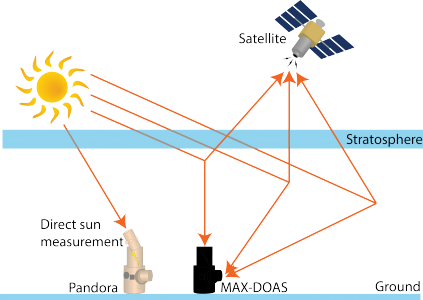
4. Chemical fingerprint of Arctic greening
Objectives:
- Provide ground validation of satellite HCHO observations at high latitudes
- Understand trend of BVOC emissions in Arctic as a result of Arctic greening
- Determine the major drivers of BVOC emission trend in Arctic and its possible impact on atmospheric composition
Approach:
- Use Pandora, MAXDOAS, and satellite observations to evaluate HCHO variability in Arctic
- Use ground, satellite and global models to determine BVOC emissions and long-term trends
- Use global models to determine the impact of Arctic greening on atmospheric composition
People:
- Tianlang Zhao (PhD student), and collaborators including Bill Simpson (UAF), Bob Swap (NASA GSFC), Gonzalo Gonzalez Abad (Harvard CFA), Caroline R Nowlan(Harvard CFA).
Funding:
- NASA
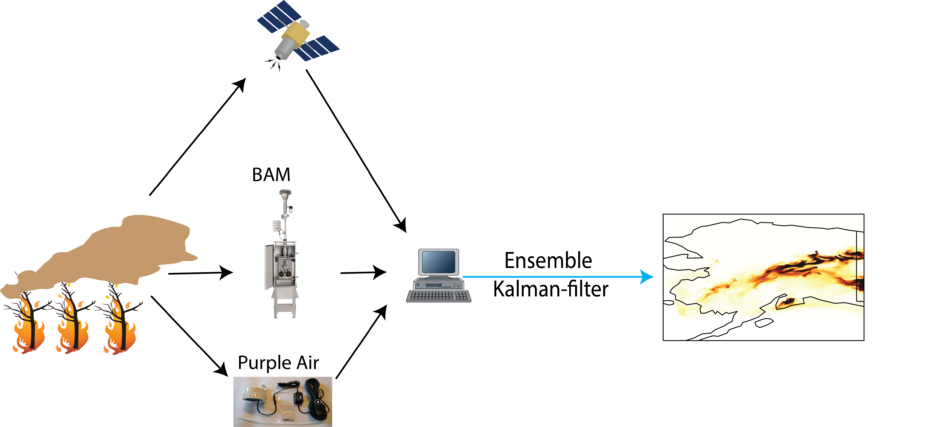
5. Improving air quality forecast during fire season
Objectives:
- Improve air quality forecast during Alaska fire seasons with surface and space observations
- Improve air quality forecast with multiple models and advanced statistical methods
- Develop relationship between surface PM2.5 and satellite AOD during fire season
People:
- Zhiwei Dong (PhD student), and collaborators including Jun Wang (U of Iowa), Martin Stuefer (UAF) and Ed Hyer(Naval Research Laboratory).
Funding:
- NASA